Unlocking the Connection: Gut Health and its Impact on Brain Function
Gut health and its connection to brain function sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. As we delve into the intricate relationship between our gut and brain, a world of fascinating discoveries awaits.
Exploring the profound effects of gut health on brain function opens up a realm of possibilities for enhancing our overall well-being and cognitive abilities.
Gut Health Overview
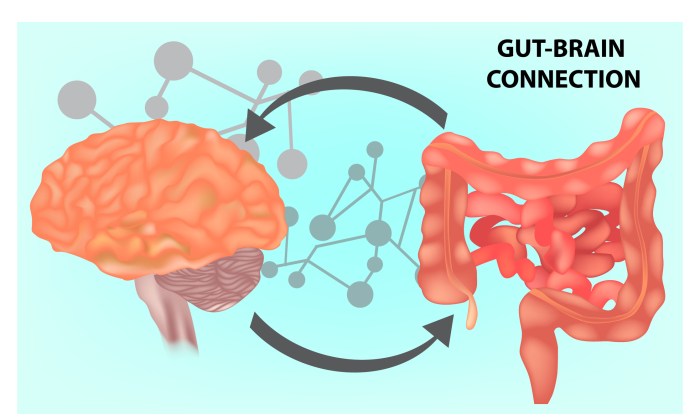
Gut health plays a crucial role in maintaining overall well-being as it is closely connected to various aspects of our health, including digestion, immunity, and even brain function.
The gut microbiome, which consists of trillions of microorganisms living in our digestive tract, plays a key role in supporting our immune system, aiding in digestion, and even influencing our mood and cognitive function.
Factors Impacting Gut Health
Several factors can impact the health of our gut microbiome and overall gut health:
- Poor Diet: Consuming a diet high in processed foods, sugar, and low in fiber can negatively affect the balance of good and bad bacteria in the gut.
- Stress: Chronic stress can disrupt the balance of gut bacteria and lead to gut inflammation.
- Antibiotics: Overuse of antibiotics can kill off beneficial bacteria in the gut, disrupting its delicate balance.
- Lack of Sleep: Inadequate sleep can impact the diversity of gut bacteria and contribute to gut dysbiosis.
- Physical Inactivity: A sedentary lifestyle can negatively impact gut health by reducing microbial diversity.
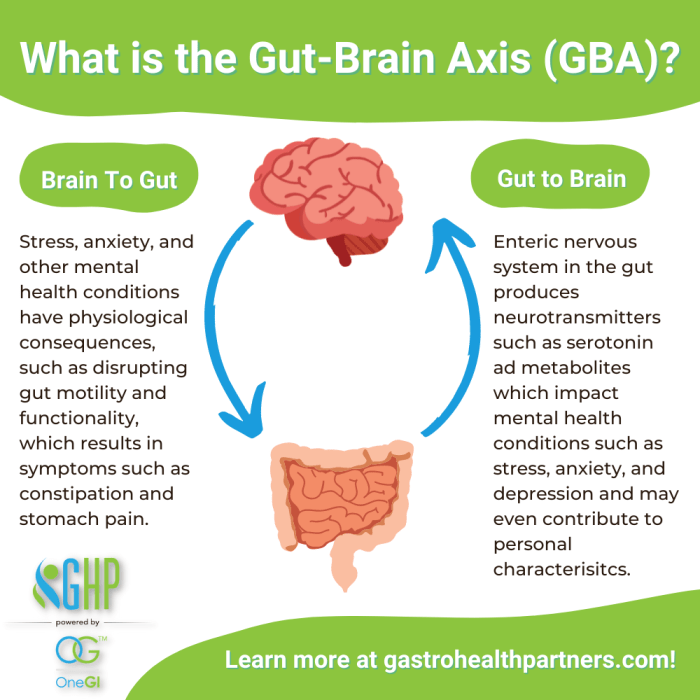
Gut-Brain Axis
The gut-brain axis is a bidirectional communication system that connects the gut and the brain. This complex network involves the central nervous system, the enteric nervous system (ENS) in the gut, and the gut microbiota, which play a crucial role in regulating various physiological processes.The gut communicates with the brain through multiple pathways, including the vagus nerve, immune system signaling, and the production of neurotransmitters and hormones.
For example, the vagus nerve serves as a direct line of communication between the gut and the brain, transmitting signals that can influence mood, behavior, and cognitive function.
Influence of Gut Health on Brain Function
Maintaining good gut health is essential for optimal brain function. Here are some examples of how gut health can influence brain function:
- Microbiota Composition: The balance of gut bacteria can impact the production of neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine, which play a key role in regulating mood and behavior. An imbalance in gut bacteria has been linked to conditions like depression and anxiety.
- Immune System Regulation: The gut is home to a large portion of the body's immune system. A healthy gut can help regulate immune responses and reduce inflammation, which is linked to cognitive decline and neurodegenerative diseases.
- Brain Development: Studies have shown that the gut microbiota can influence brain development, particularly in early life. Imbalances in gut bacteria during critical developmental periods may have long-term effects on cognitive function.
- Stress Response: The gut-brain axis is involved in the body's response to stress. Chronic stress can disrupt the balance of gut bacteria and lead to changes in brain function, contributing to conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and other stress-related disorders.
Gut Health and Mental Health
The connection between gut health and mental health is a fascinating area of research that has gained significant attention in recent years. The gut-brain axis plays a crucial role in this relationship, highlighting how the health of our gut can impact our mental well-being.Gut microbiota, the diverse community of microorganisms living in our digestive system, have been found to influence mood and emotions.
These microbes produce neurotransmitters like serotonin, often referred to as the "happy hormone," which plays a key role in regulating mood. An imbalance in gut bacteria can lead to disruptions in serotonin production, potentially contributing to mood disorders such as anxiety and depression.
Impact on Mental Health
Research has shown a strong correlation between gut health and mental health conditions like anxiety and depression. Studies have found that individuals with gastrointestinal issues are more likely to experience symptoms of anxiety and depression. Furthermore, changes in gut microbiota composition have been linked to alterations in brain chemistry and behavior, highlighting the intricate connection between the gut and the brain.
- One study published in the journal Molecular Psychiatry found that individuals with depression had lower levels of certain beneficial gut bacteria compared to healthy individuals.
- Another study published in the journal Psychopharmacology reported that probiotics, which help maintain a healthy balance of gut bacteria, showed potential in reducing symptoms of anxiety and depression.
- Research also suggests that a diet rich in fiber and fermented foods can promote a healthy gut microbiome, potentially improving mental health outcomes.
Nutritional Impact
Maintaining a healthy gut is closely tied to the foods we eat. Nutrition plays a crucial role in supporting the balance of gut bacteria and overall gut health. A diet rich in fiber, prebiotics, and probiotics can help promote a diverse and healthy gut microbiome, which in turn can benefit brain function.
Role of Nutrition in Gut Health
A diet high in fiber from fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes can provide the necessary fuel for beneficial gut bacteria to thrive. Prebiotics, found in foods like garlic, onions, bananas, and asparagus, serve as food for probiotics and help stimulate their growth.
Probiotics, which are live bacteria found in fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, and sauerkraut, can introduce beneficial bacteria into the gut, supporting a healthy microbiome.
Foods that Promote Good Gut Health
Fiber-rich foods
Whole grains, fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds
Prebiotic foods
Garlic, onions, leeks, bananas, asparagus
Probiotic foods
Yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi, miso, tempeh
Effects of Balanced Diet vs. Processed Foods on Gut Health and Brain Function
A balanced diet rich in whole, nutrient-dense foods can support a healthy gut microbiome, leading to improved gut health and potentially enhanced brain function. On the other hand, a diet high in processed foods, sugar, and unhealthy fats can disrupt the balance of gut bacteria, leading to inflammation and potential negative effects on both gut health and brain function.
Lifestyle Factors

Our lifestyle choices play a significant role in the health of our gut, which in turn affects our brain function. Factors such as stress, sleep, and exercise can have a profound impact on our gut health and overall well-being.
Stress
Chronic stress can disrupt the balance of bacteria in the gut, leading to inflammation and digestive issues. This can weaken the gut lining and contribute to leaky gut syndrome. To reduce stress and improve gut health, consider incorporating stress-reducing activities into your daily routine such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, or yoga.
Sleep
Poor sleep patterns can negatively impact the diversity of gut bacteria and increase inflammation in the gut. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night to support a healthy gut microbiome. Establishing a consistent sleep schedule and creating a relaxing bedtime routine can help improve your sleep quality and gut health.
Exercise
Regular physical activity has been shown to promote the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut and reduce inflammation. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week to support a healthy gut microbiome. Incorporating a combination of aerobic exercise, strength training, and flexibility exercises can have a positive impact on both gut health and brain function.
Last Recap
In conclusion, the intricate interplay between gut health and brain function underscores the importance of nurturing our digestive system for optimal mental performance. By embracing a holistic approach to health that prioritizes gut health, we pave the way for a brighter future filled with vitality and clarity of mind.
FAQ Compilation
How does gut health impact brain function?
Gut health can influence brain function through the gut-brain axis, where the gut microbiota communicates with the brain, affecting mood, cognitive abilities, and mental health.
What are some lifestyle factors that can improve gut health?
Factors such as managing stress, getting adequate sleep, and engaging in regular exercise can positively impact gut health and consequently enhance brain function.
Which foods promote good gut health?
Foods rich in fiber, probiotics, and prebiotics like fruits, vegetables, yogurt, and whole grains support a healthy gut microbiome and contribute to better brain function.

