How stress impacts your hormonal health: Exploring the Connection
Exploring the intricate relationship between stress and hormonal health, this article delves into the profound impact that stress can have on our body's delicate hormonal balance. From the subtle shifts in hormone levels to the potential health consequences, understanding this connection is crucial for overall well-being.
As we navigate through the complexities of hormonal health and stress, we uncover fascinating insights that shed light on how our body responds to different stressors and the cascade of effects on our hormonal system.
Introduction to Hormonal Health and Stress
Hormonal health refers to the balance and proper functioning of hormones in the body, which play a crucial role in regulating various bodily functions such as metabolism, growth, mood, and reproduction. Maintaining hormonal balance is essential for overall health and well-being.
Stress is a natural response to challenging or threatening situations, triggering the release of stress hormones like cortisol and adrenaline. While stress can be beneficial in short bursts, chronic stress can have detrimental effects on the body, including disrupting hormonal balance.
Examples of Hormones Affected by Stress
- Cortisol: Known as the primary stress hormone, cortisol is released in response to stress and helps regulate metabolism, immune response, and blood pressure.
- Adrenaline: Also known as epinephrine, adrenaline is released during the body's fight-or-flight response to stress, increasing heart rate and providing a burst of energy.
- Insulin: Chronic stress can affect insulin sensitivity, leading to imbalances in blood sugar levels and potentially contributing to conditions like diabetes.
- Progesterone and Estrogen: Stress can disrupt the balance of these reproductive hormones, affecting menstrual cycles and fertility in women.
- Testosterone: Prolonged stress can lower testosterone levels in both men and women, impacting libido, muscle mass, and mood.
The Stress Response System
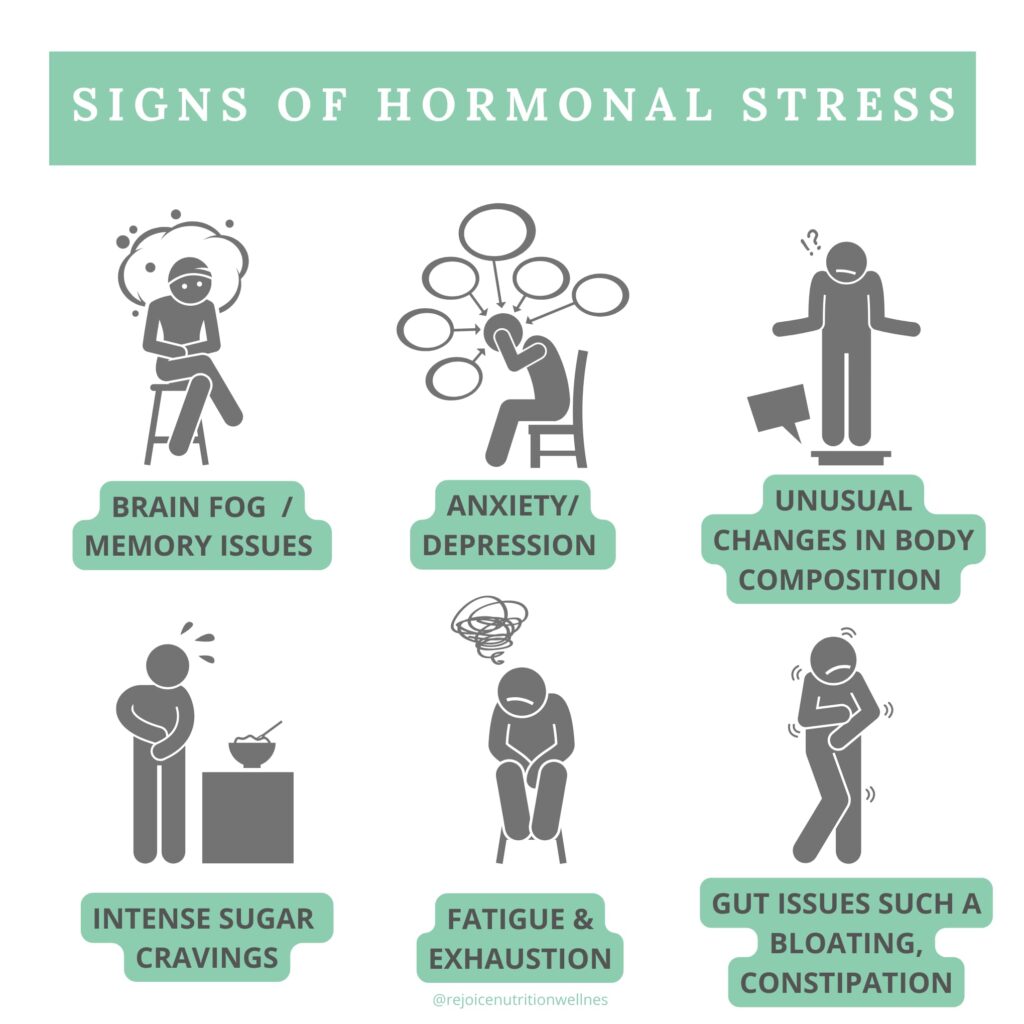
Stress triggers a complex chain of events in the body known as the stress response system. This system is designed to help us cope with stressful situations by releasing hormones and neurotransmitters that prepare the body for action.Cortisol, often referred to as the "stress hormone," plays a crucial role in the stress response system.
When we encounter a stressful situation, the brain signals the adrenal glands to release cortisol into the bloodstream. Cortisol helps regulate metabolism, immune response, and blood pressure, among other functions.Chronic stress can have a profound impact on the stress response system.
Prolonged exposure to stress can lead to dysregulation of cortisol levels, with the body either producing too much or too little cortisol. This dysregulation can disrupt the body's natural balance and lead to a variety of health issues, including anxiety, depression, weight gain, and immune system suppression.
Impact of Stress on Endocrine Glands

Stress can significantly impact the function of various endocrine glands in the body, leading to hormonal imbalances and disrupting normal bodily processes. The endocrine system is responsible for producing and regulating hormones that control various functions such as metabolism, growth, reproduction, and stress response.
Examples of Endocrine Glands Impacted by Stress
- The adrenal glands, located on top of each kidney, play a crucial role in the body's stress response by producing hormones like cortisol and adrenaline. Chronic stress can lead to overactivation of the adrenal glands, resulting in excess cortisol production, which can have negative effects on the body.
- The thyroid gland, which regulates metabolism, can also be affected by stress. High levels of stress hormones can disrupt the production of thyroid hormones, leading to issues like hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism.
- The pituitary gland, often referred to as the "master gland," regulates the function of other endocrine glands. Prolonged stress can impact the pituitary gland's ability to release hormones that control various bodily functions.
Link Between Stress and Hormonal Imbalances
Chronic stress can result in hormonal imbalances by disrupting the intricate balance of hormones in the body. Elevated levels of stress hormones like cortisol can interfere with the normal functioning of the endocrine system, leading to issues such as irregular menstrual cycles, weight gain, mood swings, and compromised immune function.
It is essential to manage stress effectively to maintain the health and proper functioning of the endocrine system.
Specific Hormones Affected by Stress
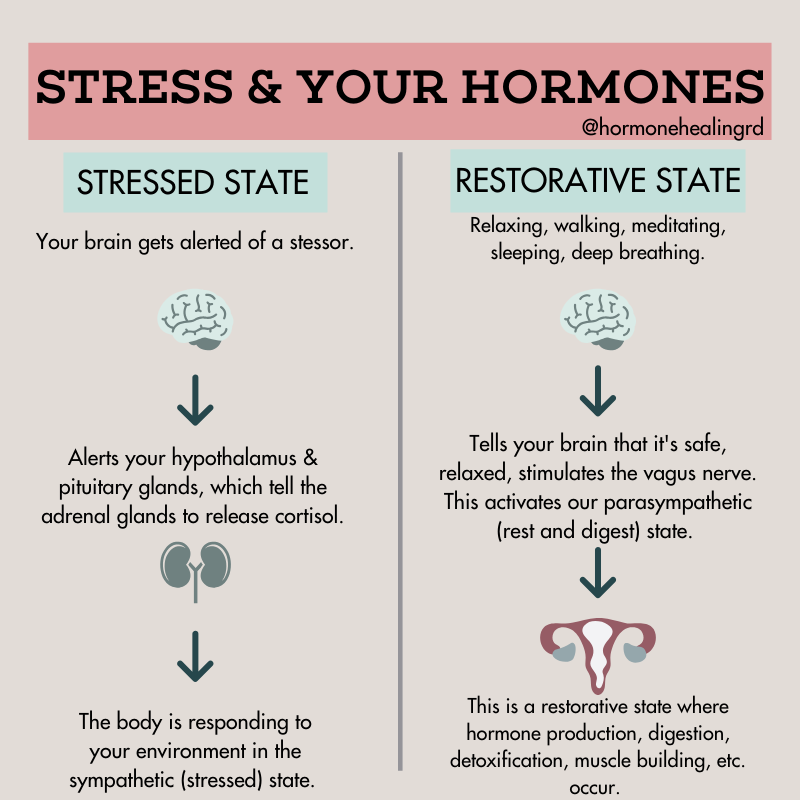
Stress can have a significant impact on various hormones in the body, leading to imbalances that can affect overall health. Some hormones are particularly sensitive to stress, and understanding how stress influences their production is crucial for managing hormonal health
Cortisol
Cortisol, often referred to as the "stress hormone," is released by the adrenal glands in response to stress. Chronic stress can lead to consistently high levels of cortisol, which can disrupt various bodily functions. Imbalanced cortisol levels can impact metabolism, immune function, and even cognitive processes.
Adrenaline
Adrenaline, also known as epinephrine, is another hormone produced by the adrenal glands in response to stress. It triggers the body's "fight or flight" response, increasing heart rate and blood flow to muscles. Prolonged stress can lead to excess adrenaline production, contributing to anxiety, insomnia, and cardiovascular issues.
Insulin
Stress can also influence insulin levels, the hormone responsible for regulating blood sugar. Chronic stress can lead to insulin resistance, affecting the body's ability to manage glucose effectively. This imbalance can increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes and other metabolic disorders.
Thyroid Hormones
The thyroid gland, which produces hormones that regulate metabolism, can be impacted by stress as well. High levels of stress can disrupt the production of thyroid hormones, leading to symptoms such as fatigue, weight changes, and mood disturbances. Imbalanced thyroid hormones can also affect overall energy levels and cognitive function.
Reproductive Hormones
Stress can also affect reproductive hormones, such as estrogen and testosterone. Chronic stress can disrupt the menstrual cycle in women and reduce libido in both men and women. Imbalanced reproductive hormones can impact fertility, sexual function, and overall reproductive health.
Health Conditions Resulting from Hormonal Imbalance due to Stress
Stress-induced hormonal changes can have a significant impact on our overall health, leading to various health conditions. These conditions can arise from the disruption of the delicate balance of hormones in our body caused by chronic stress.
Common Health Conditions Associated with Hormonal Imbalance
- Insomnia: Elevated levels of cortisol, the stress hormone, can interfere with sleep patterns, leading to insomnia.
- Weight Gain: Stress-induced cortisol release can contribute to weight gain, particularly in the abdominal area.
- Depression and Anxiety: Imbalances in hormones such as serotonin and dopamine can lead to mood disorders.
- Heart Disease: Chronic stress can increase the risk of heart disease through hormonal imbalances affecting blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
How Stress-Induced Hormonal Changes Contribute to Health Conditions
Stress triggers the release of hormones like cortisol and adrenaline, designed to help us deal with immediate threats. However, chronic stress can lead to continuous elevation of these hormones, disrupting the normal hormonal balance in the body. This imbalance can then contribute to the development of various health conditions.
Managing Health Conditions through Stress Management Techniques
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity can help reduce stress levels and regulate hormone production.
- Healthy Diet: Eating a balanced diet can support hormone balance and overall well-being.
- Mindfulness and Meditation: Practices like mindfulness and meditation can help reduce stress and promote hormonal balance.
- Adequate Sleep: Prioritizing good sleep hygiene can help regulate hormone levels and support overall health.
Last Recap
In conclusion, the intricate interplay between stress and hormonal health highlights the importance of managing stress effectively to maintain a harmonious balance within our body. By adopting healthy coping mechanisms and lifestyle choices, we can safeguard our hormonal well-being and overall health in the long run.
FAQ Insights
How does stress affect hormone levels?
Stress triggers the release of cortisol and adrenaline, which can disrupt the normal production and balance of hormones in the body.
Can hormonal imbalance due to stress be reversed?
With effective stress management techniques, hormonal imbalance caused by stress can be gradually reversed over time.
What are some common health conditions associated with stress-induced hormonal imbalance?
Conditions like adrenal fatigue, thyroid disorders, and reproductive issues are often linked to hormonal imbalances caused by chronic stress.




