How Air Quality at Home Affects Your Respiratory Health: A Comprehensive Guide
Exploring the intricate relationship between air quality at home and respiratory health unveils a crucial aspect of our well-being. As we delve into the impact of indoor air pollution on conditions like asthma and allergies, it becomes evident why ensuring good air quality is paramount for a healthy respiratory system.
This guide will shed light on the sources of indoor air pollution, the effects of poor air quality on respiratory health, strategies to improve air quality, and how to monitor and maintain a healthy indoor environment.
Introduction to Air Quality at Home and Respiratory Health
Air quality at home refers to the level of pollutants, allergens, and irritants present in the air within your living space. It encompasses factors such as dust, pet dander, mold spores, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and tobacco smoke.
Good air quality is crucial for maintaining optimal respiratory health. Breathing in clean air is essential for the proper functioning of our lungs and overall well-being. Poor air quality at home can lead to a variety of respiratory health issues, exacerbate existing conditions, and increase the risk of developing respiratory diseases.
Common Respiratory Health Issues Linked to Poor Air Quality at Home
- 1. Asthma Exacerbation: Poor air quality can trigger asthma symptoms and exacerbate asthma attacks, leading to difficulty breathing, wheezing, and chest tightness.
- 2. Allergic Rhinitis: Exposure to allergens like dust mites, pet dander, and mold spores in indoor air can cause allergic rhinitis symptoms such as sneezing, nasal congestion, and itchy eyes.
- 3. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD): Individuals with COPD may experience worsened symptoms when exposed to indoor air pollutants, leading to increased coughing, mucus production, and shortness of breath.
- 4. Respiratory Infections: Poor air quality can increase the risk of respiratory infections such as bronchitis and pneumonia, especially in vulnerable populations like children, the elderly, and individuals with weakened immune systems.
Sources of Indoor Air Pollution
Indoor air pollution can arise from various sources within our homes, impacting both air quality and respiratory health. It is essential to be aware of these sources to take necessary steps to mitigate their effects.
Tobacco Smoke
Tobacco smoke is a significant source of indoor air pollution, releasing harmful chemicals and particulate matter into the air. Secondhand smoke can lead to respiratory issues such as asthma exacerbation, bronchitis, and even lung cancer.
Cooking Fumes
Cooking fumes, especially from high-heat cooking methods like frying, can produce pollutants like volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and particulate matter. Prolonged exposure to these fumes can irritate the respiratory system and worsen conditions like allergies and asthma.
Mold
Mold growth in damp or poorly ventilated areas of the home can release spores and mycotoxins into the air. Inhalation of mold spores can trigger allergies, asthma attacks, and respiratory infections, posing a threat to respiratory health.
Examples of Indoor Pollutants and Their Effects
- Airborne allergens like dust mites and pet dander can trigger allergic reactions and exacerbate asthma symptoms.
- Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) from household products like cleaning agents and air fresheners can cause respiratory irritation and headaches.
- Carbon monoxide (CO) from gas stoves and heating systems can lead to symptoms like dizziness, nausea, and even death in high concentrations.
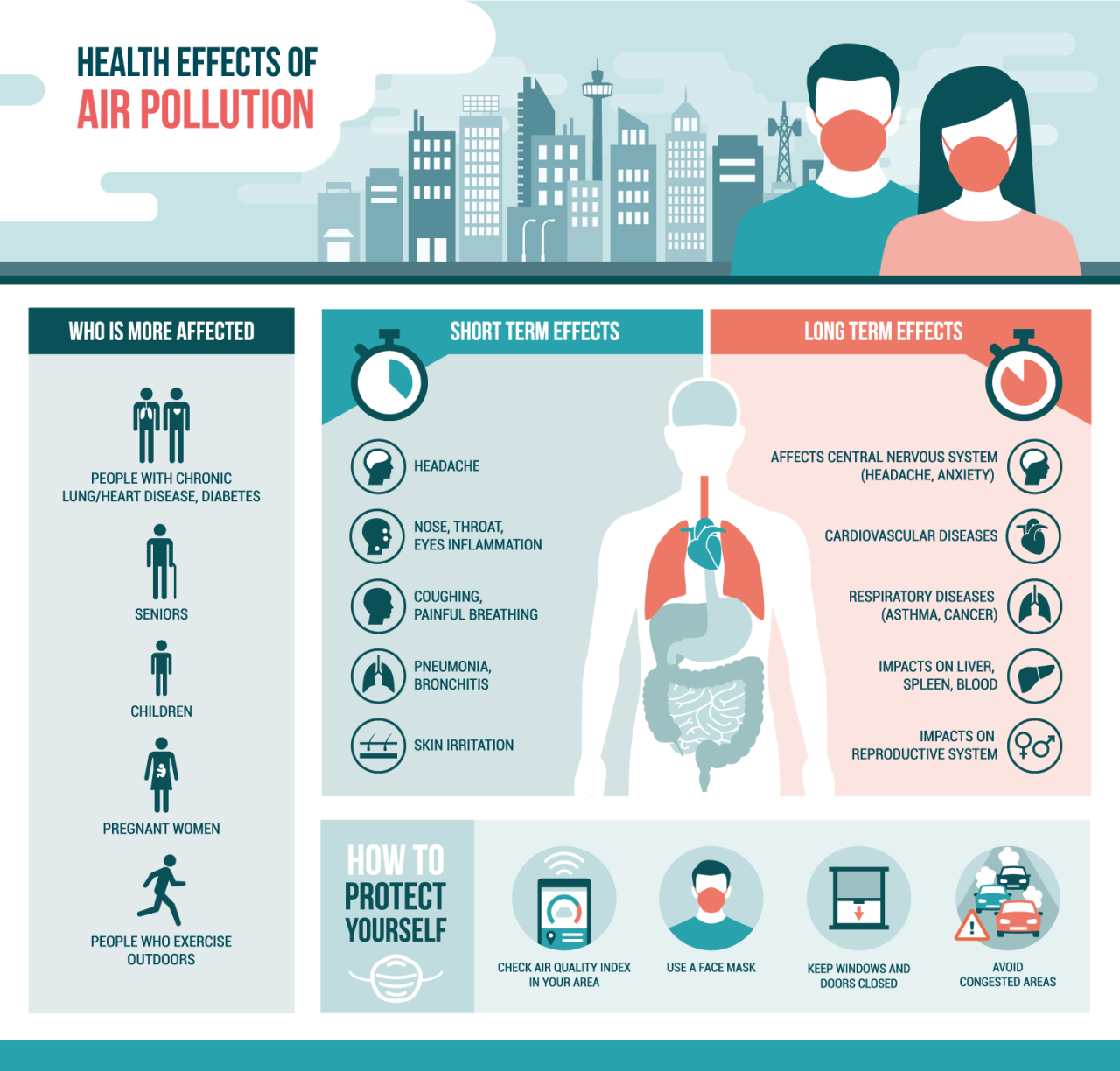
Effects of Poor Air Quality on Respiratory Health
Poor air quality can have detrimental effects on respiratory health, particularly for individuals with conditions like asthma or allergies. When indoor air is polluted with particles, chemicals, or allergens, it can trigger or worsen symptoms, leading to difficulty breathing, coughing, wheezing, and other respiratory issues.
Exacerbation of Respiratory Conditions
Exposure to indoor air pollution can exacerbate existing respiratory conditions such as asthma or allergies. The presence of irritants in the air can trigger inflammation in the airways, making it harder for individuals to breathe comfortably. This can result in increased asthma attacks, allergic reactions, and overall discomfort for those affected.
Long-Term Effects on the Respiratory System
Prolonged exposure to poor indoor air quality can have long-term effects on the respiratory system. Studies have shown that individuals who are regularly exposed to indoor air pollution are at a higher risk of developing chronic respiratory conditions, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) or even lung cancer.
Additionally, poor air quality can lead to decreased lung function over time, making it harder for individuals to breathe efficiently.
Correlation Between Indoor Air Quality and Respiratory Health
Research has indicated a strong correlation between indoor air quality and respiratory health. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), indoor air pollution is responsible for millions of premature deaths each year, with respiratory diseases being a primary cause. In fact, a study published in the American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine found that improving indoor air quality can lead to a significant decrease in respiratory symptoms and hospitalizations for respiratory conditions.
Strategies to Improve Air Quality at Home
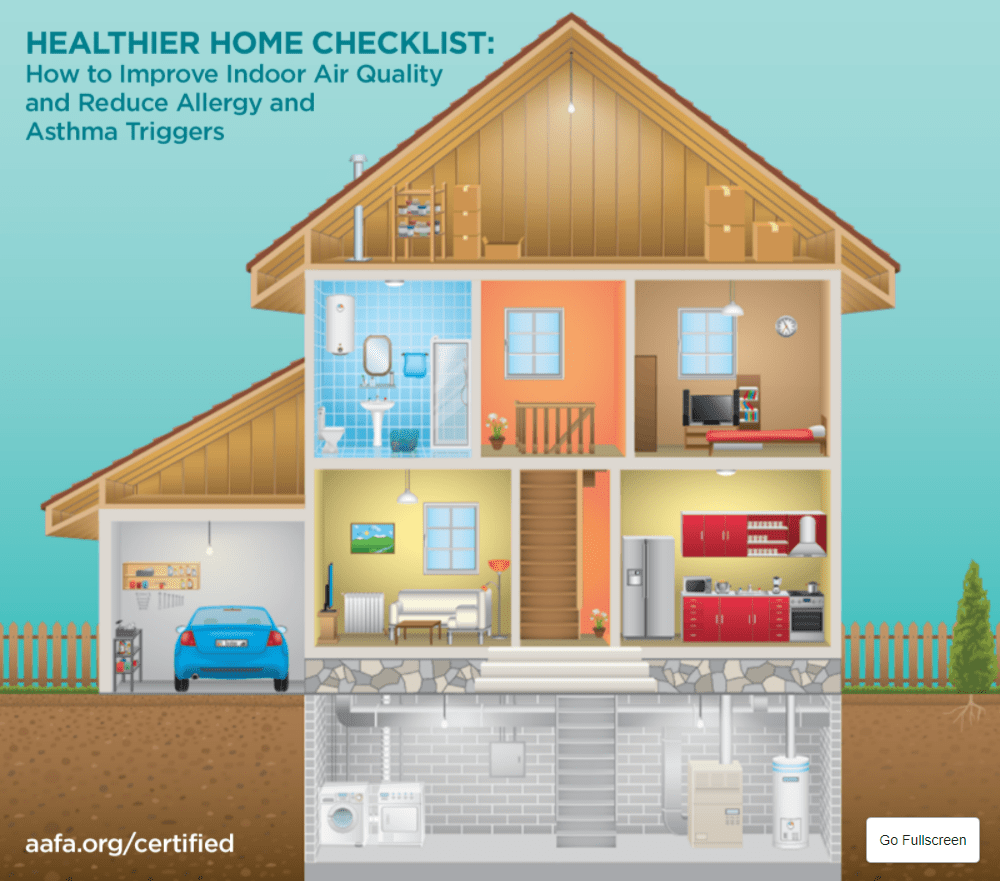
Improving air quality at home is essential for maintaining good respiratory health. By implementing practical steps and making small changes, you can create a healthier indoor environment for you and your family.
Proper Ventilation
One of the key ways to enhance indoor air quality is by ensuring proper ventilation in your home. Opening windows regularly to let fresh air in can help reduce the concentration of indoor pollutants and improve air circulation.
Air Purifiers
Consider investing in an air purifier to filter out contaminants such as dust, pollen, pet dander, and other allergens. Air purifiers can help improve air quality and reduce respiratory irritants in your home.
Indoor Plants
Indoor plants not only add a touch of greenery to your living space but also act as natural air purifiers. Plants like spider plants, peace lilies, and aloe vera can help remove toxins from the air and promote better respiratory health.
Reducing Exposure to Indoor Pollutants
Avoid smoking indoors, limit the use of harsh cleaning products with strong fumes, and regularly clean and dust your home to reduce indoor pollutants. Additionally, using natural cleaning products can help minimize exposure to harmful chemicals.
Monitoring and Maintaining Indoor Air Quality

Regular monitoring and maintenance of indoor air quality are crucial for ensuring a healthy living environment. By implementing various methods and practices, individuals can effectively improve the air quality in their homes.
Methods for Monitoring Indoor Air Quality
- Utilizing air quality monitors: These devices can measure various pollutants such as particulate matter, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), carbon monoxide, and more. By regularly checking these levels, individuals can identify potential issues and take corrective actions.
- Testing for radon: Radon is a radioactive gas that can seep into homes through the ground. Testing for radon levels can help prevent long-term health risks associated with prolonged exposure.
Importance of Regular Maintenance of HVAC Systems
Regular maintenance of heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems is essential for improving indoor air quality. By changing filters, cleaning ducts, and scheduling professional inspections, individuals can ensure that their HVAC systems are functioning efficiently and not circulating pollutants throughout the home.
Lifestyle Choices Impact on Indoor Air Quality
- Avoid smoking indoors: Smoking indoors can significantly degrade indoor air quality and increase the risk of respiratory issues.
- Proper ventilation: Ensuring adequate ventilation in the home can help remove pollutants and improve air circulation.
- Reducing use of harsh chemicals: Limiting the use of harsh cleaning products and opting for eco-friendly alternatives can help reduce indoor air pollution.
Last Word
In conclusion, understanding how air quality at home affects your respiratory health is not just informative but imperative for safeguarding your well-being. By implementing the strategies discussed and staying vigilant about indoor air quality, you can take proactive steps towards promoting a healthier respiratory system for yourself and your loved ones.
Question & Answer Hub
How can indoor air pollution impact respiratory health?
Indoor air pollution can exacerbate conditions like asthma and allergies, leading to respiratory issues and long-term health concerns.
What are some practical steps to improve air quality at home?
Installing air purifiers, ensuring proper ventilation, and incorporating indoor plants can significantly enhance indoor air quality.
Why is monitoring indoor air quality important?
Regular monitoring helps in identifying pollutants and taking corrective measures to maintain a healthy indoor environment.




