How sleep affects long-term brain health: The Crucial Connection
Exploring the intricate link between sleep and long-term brain health, this article delves into the importance of quality sleep for overall well-being. From understanding the different sleep stages to exploring the impact of sleep deprivation, we uncover how our nightly rest directly influences the health of our brains.
As we navigate through the realm of sleep and brain health, we uncover fascinating insights that shed light on the significance of a good night's sleep for our cognitive functions and overall brain function.
Introduction to Sleep and Brain Health
Sleep plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health and well-being. It is during sleep that our bodies repair and rejuvenate, allowing us to function optimally. However, the impact of sleep goes beyond just physical health; it also significantly affects our brain health.
The relationship between sleep and brain health is intricate and essential. Sleep is known to be a critical factor in various cognitive functions, including memory consolidation, learning, problem-solving, and emotional regulation. Insufficient or poor-quality sleep can impair these cognitive processes, leading to difficulties in concentration, decision-making, and overall cognitive function.
Impact of Sleep Quality on Long-term Brain Health
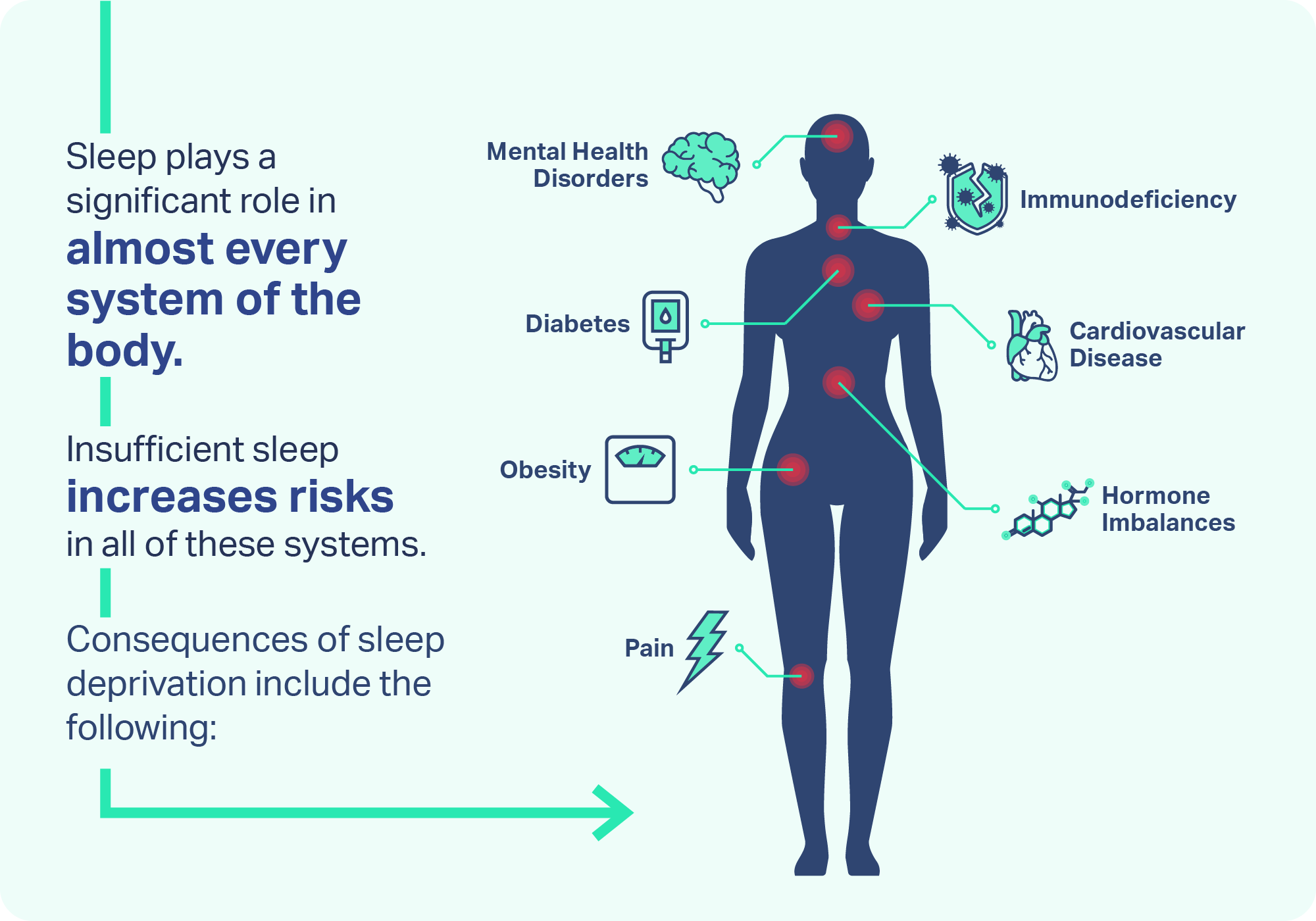
Sleep quality is directly linked to long-term brain health. Chronic sleep deprivation or disrupted sleep patterns have been associated with an increased risk of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's and dementia. During sleep, the brain clears out toxins that accumulate during waking hours, promoting neural regeneration and overall brain health.
Therefore, consistently getting restful and sufficient sleep is crucial for preserving cognitive function and reducing the risk of cognitive decline in the long run.
Sleep Stages and Brain Function
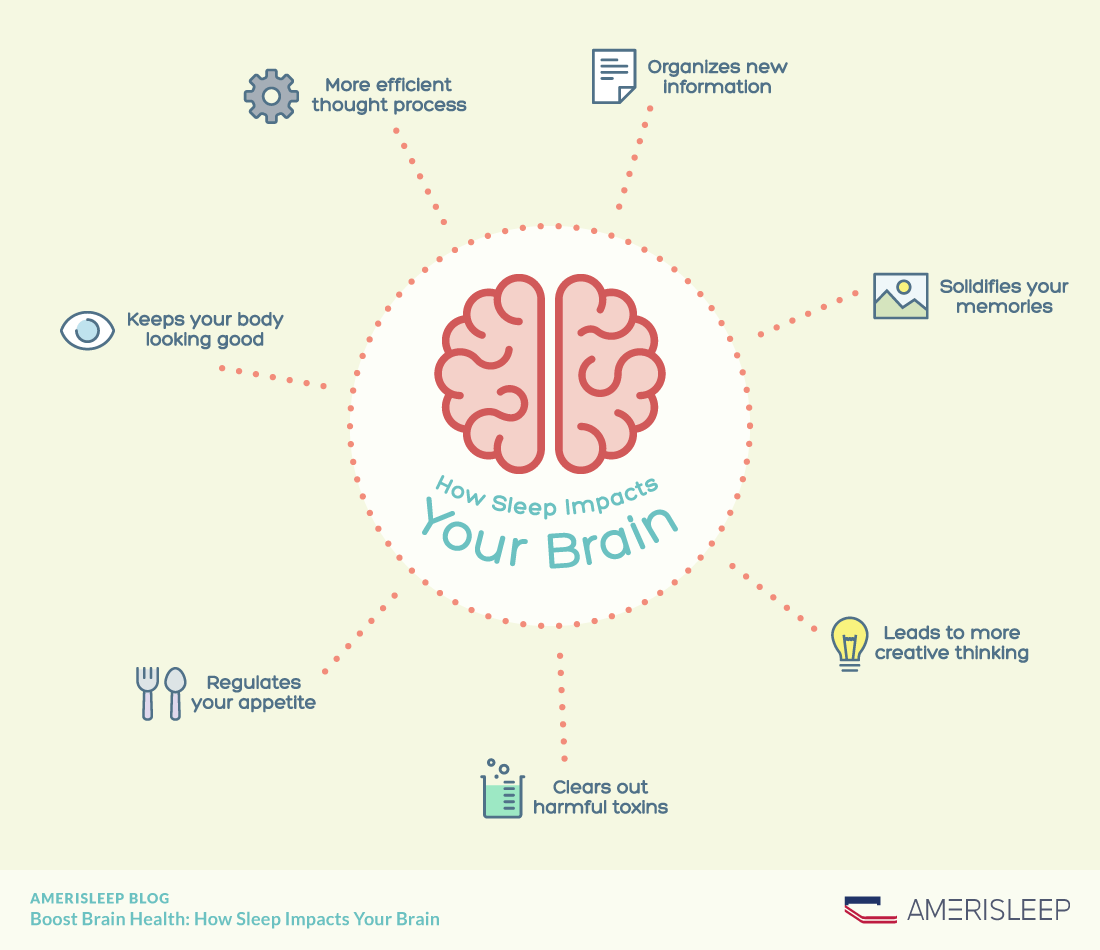
Sleep consists of several stages that play a crucial role in brain function and overall health. Each stage contributes differently to cognitive processes and memory consolidation, with REM sleep being particularly important.
NREM Sleep
NREM (non-rapid eye movement) sleep is divided into three stages: N1, N2, and N3. During these stages, the body repairs and regrows tissues, builds bone and muscle, and strengthens the immune system. NREM sleep also plays a role in maintaining cognitive function and emotional well-being.
REM Sleep
REM (rapid eye movement) sleep is the stage where most dreaming occurs. This stage is crucial for memory consolidation and learning processes. During REM sleep, the brain processes and stores information from the day, making it easier to recall and use this information in the future.
Lack of REM sleep has been linked to memory deficits and cognitive impairment.
Role of REM Sleep in Memory Consolidation
During REM sleep, the brain forms new neural connections and consolidates memories. This process helps in organizing and storing information, leading to improved cognitive function and problem-solving skills. REM sleep is essential for overall brain health and plays a significant role in maintaining optimal cognitive abilities.
Impact of Sleep Deprivation on Brain Health
Chronic sleep deprivation can have severe consequences on brain health, impacting various cognitive functions and overall well-being.
Effects of Chronic Sleep Deprivation on the Brain
- Impaired memory consolidation: Lack of sleep can hinder the brain's ability to consolidate and store memories, affecting learning and retention.
- Reduced cognitive performance: Sleep deprivation can lead to decreased focus, attention, and problem-solving skills, impacting overall cognitive function.
- Increased risk of mood disorders: Insufficient sleep has been linked to an increased risk of anxiety, depression, and irritability due to altered brain chemistry.
How Lack of Sleep Affects Cognitive Function, Mood, and Decision-Making
- Cognitive function: Sleep deprivation impairs cognitive processes such as decision-making, problem-solving, and creativity, leading to reduced efficiency in daily tasks.
- Mood disturbances: Inadequate sleep can disrupt the brain's emotional regulation, resulting in mood swings, irritability, and heightened stress levels.
- Decision-making: Sleep-deprived individuals may exhibit poor judgment, impulsivity, and risk-taking behaviors due to compromised cognitive abilities.
Long-Term Consequences of Inadequate Sleep on the Brain
- Neurodegenerative diseases: Prolonged sleep deprivation has been associated with an increased risk of neurodegenerative conditions such as Alzheimer's disease due to the accumulation of toxic proteins in the brain.
- Cognitive decline: Chronic lack of sleep can accelerate cognitive decline and impair brain function over time, leading to difficulties in memory, concentration, and decision-making.
- Emotional disturbances: Persistent sleep deprivation can contribute to long-term mood disorders, anxiety, and depression, affecting overall mental health and well-being.
Sleep Disorders and Brain Health
Sleep disorders can have a significant impact on long-term brain health. Conditions like insomnia and sleep apnea can disrupt normal brain function, leading to cognitive issues and other health problems. It is crucial to understand how these disorders affect the brain and what treatment options are available to mitigate their effects.
Common Sleep Disorders
- Insomnia: Characterized by difficulty falling or staying asleep, insomnia can lead to cognitive impairment, mood disturbances, and overall decreased brain function.
- Sleep Apnea: A condition where breathing repeatedly stops and starts during sleep, sleep apnea can result in poor oxygenation of the brain, leading to memory problems and cognitive decline.
- Narcolepsy: A neurological disorder that affects the brain's ability to regulate sleep-wake cycles, narcolepsy can cause sudden sleep attacks and excessive daytime sleepiness, impacting overall brain health.
Effects on Brain Function
- Insomnia: Chronic sleep deprivation from insomnia can impair cognitive function, memory consolidation, and emotional regulation, affecting overall brain health.
- Sleep Apnea: The intermittent lack of oxygen during sleep apnea episodes can lead to cognitive impairment, memory issues, and an increased risk of neurodegenerative diseases.
- Narcolepsy: Disrupted sleep patterns in narcolepsy can result in fragmented sleep, leading to difficulties in concentration, memory recall, and overall brain performance.
Treatment Options
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia (CBT-I): A structured program that helps individuals address the underlying causes of insomnia and improve sleep habits, promoting better brain health.
- Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) Therapy for Sleep Apnea: A treatment that uses a machine to deliver a constant airflow to keep the airway open during sleep, improving oxygenation of the brain and reducing cognitive impairments.
- Medications and Lifestyle Changes: Depending on the specific sleep disorder, medications or lifestyle modifications like regular exercise, healthy diet, and stress management techniques can also help improve sleep quality and brain function.
Sleep Hygiene Practices for Optimal Brain Health
Maintaining good sleep hygiene practices is crucial for ensuring optimal brain health. By following a consistent routine and creating a sleep-conducive environment, you can promote healthy brain function and overall well-being.
1. Consistent Sleep Schedule
Maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, even on weekends, helps regulate your body's internal clock. This consistency supports the natural sleep-wake cycle, known as the circadian rhythm, which plays a vital role in brain health. Going to bed and waking up at the same time each day can improve the quality of your sleep and enhance cognitive function.
2. Limiting Stimulants and Electronics Before Bed
Avoiding stimulants like caffeine and electronic devices before bedtime can help you unwind and prepare your body for sleep. The blue light emitted by screens can disrupt the production of melatonin, a hormone that regulates sleep. Creating a calming bedtime routine, such as reading a book or taking a warm bath, can signal to your brain that it's time to rest.
3. Comfortable Sleep Environment
Creating a sleep-conducive environment is essential for optimizing brain function during sleep. Keep your bedroom cool, dark, and quiet to promote uninterrupted rest. Invest in a comfortable mattress and pillows to support proper sleep posture. Eliminate any distractions, such as noise or light, that may disrupt your sleep cycle.
4. Regular Exercise
Engaging in regular physical activity can improve sleep quality and contribute to better brain health. Exercise helps regulate mood, reduce stress, and promote relaxation, all of which are essential for a good night's sleep. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week to reap the benefits of improved sleep and cognitive function.
5. Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques
Incorporating mindfulness practices and relaxation techniques into your daily routine can help reduce stress and promote relaxation before bedtime. Techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, or gentle yoga can calm the mind and body, making it easier to fall asleep and stay asleep throughout the night.
6. Healthy Diet and Hydration
Eating a balanced diet and staying hydrated can also impact your sleep quality and brain health. Avoid heavy meals close to bedtime and opt for light snacks if you're hungry before sleep. Limiting alcohol and caffeine intake, especially in the evening, can prevent disruptions in your sleep patterns and support overall brain function.
Final Review
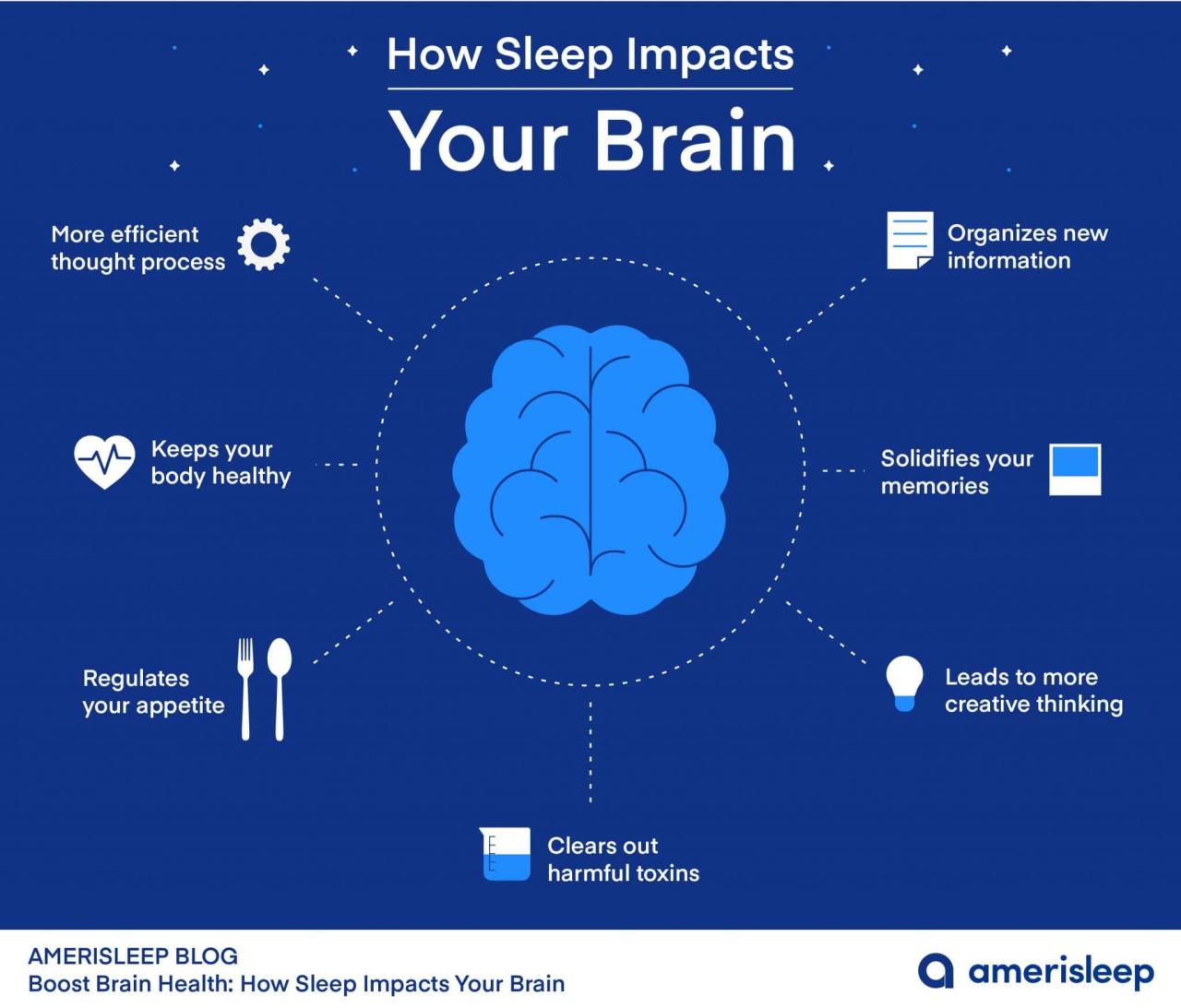
In conclusion, the discussion around how sleep affects long-term brain health leaves us with a profound understanding of the critical role sleep plays in maintaining cognitive abilities and overall brain function. By prioritizing good sleep hygiene practices, we can pave the way for a healthier brain and a sharper mind in the long run.
Common Queries
How does poor sleep quality impact long-term brain health?
Poor sleep quality can lead to cognitive decline, memory issues, and increased risk of neurodegenerative diseases over time.
What are some common sleep disorders that can affect brain health?
Common sleep disorders like insomnia, sleep apnea, and narcolepsy can significantly impact long-term brain health.
How can maintaining a consistent sleep schedule benefit brain health?
Consistent sleep schedules help regulate circadian rhythms, leading to better cognitive function and overall brain health.
What role does REM sleep play in memory consolidation?
REM sleep is crucial for memory consolidation and plays a vital role in cognitive function and learning processes.




