Top Nutrition Plans for Heart Health: A Comprehensive Guide
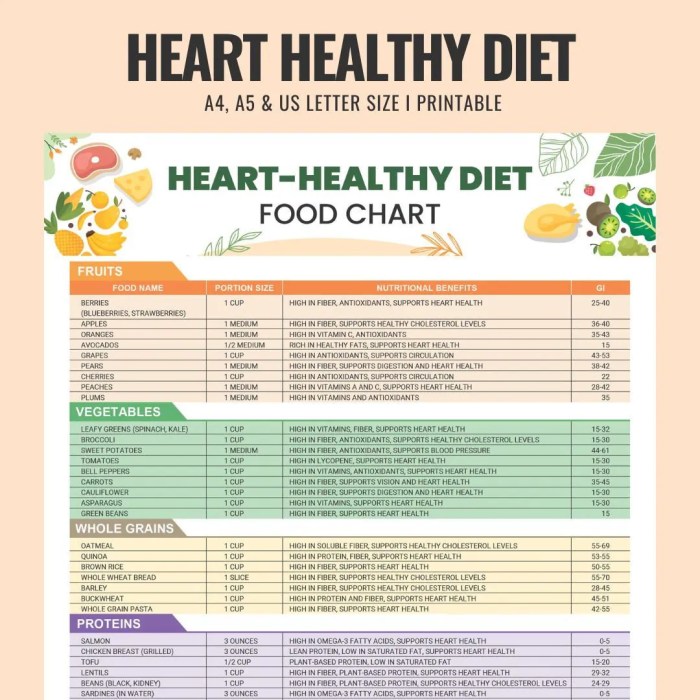
Exploring the realm of top nutrition plans for heart health unveils a treasure trove of information aimed at enhancing cardiovascular well-being. This guide promises to delve into key aspects of nutrition that play a crucial role in maintaining a healthy heart, offering insights into popular diets like the Mediterranean, DASH, plant-based, and low-sodium options.
Let's embark on a journey towards optimal heart health through mindful dietary choices.
Overview of Heart-Healthy Nutrition Plans
Proper nutrition plays a crucial role in maintaining heart health and reducing the risk of cardiovascular diseases. A heart-healthy diet can help manage cholesterol levels, blood pressure, and overall heart function.
Key Components of a Heart-Healthy Diet
- Focus on fruits and vegetables: These are rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that support heart health.
- Choose whole grains: Whole grains provide fiber, which helps lower cholesterol and improve heart function.
- Include lean proteins: Opt for sources like fish, poultry, nuts, and legumes to reduce saturated fats in the diet.
- Limit unhealthy fats: Reduce intake of trans fats and saturated fats found in processed foods, fried foods, and baked goods.
- Watch sodium intake: Excess salt can increase blood pressure, so it's important to limit sodium consumption.
Foods Beneficial for Heart Health
- Fatty fish: Rich in omega-3 fatty acids, fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and trout can lower the risk of heart disease.
- Berries: Packed with antioxidants, berries like blueberries, strawberries, and raspberries can help reduce inflammation and improve heart health.
- Nuts: Almonds, walnuts, and pistachios are good sources of healthy fats, fiber, and antioxidants that benefit heart health.
- Leafy greens: Spinach, kale, and collard greens are high in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that support heart health.
- Olive oil: Rich in monounsaturated fats, olive oil can help lower cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of heart disease.
Mediterranean Diet
The Mediterranean diet is a heart-healthy eating plan inspired by the traditional dietary patterns of countries bordering the Mediterranean Sea. It emphasizes consuming fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, seeds, olive oil, and moderate amounts of fish and poultry. Red meat and sweets are limited in this diet.
Foods Included in the Mediterranean Diet
- Fruits and vegetables: These provide essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that support heart health.
- Whole grains: Foods like whole wheat, brown rice, and oats offer fiber and nutrients that are beneficial for the heart.
- Legumes: Beans, lentils, and chickpeas are excellent sources of protein and fiber, aiding in heart health.
- Nuts and seeds: Almonds, walnuts, chia seeds, and flaxseeds provide healthy fats and nutrients that support heart function.
- Olive oil: This heart-healthy fat is a staple in the Mediterranean diet, offering monounsaturated fats and antioxidants.
- Fish and poultry: Lean protein sources like fish and chicken are preferred over red meat in this diet.
The Mediterranean diet has been linked to numerous health benefits, particularly in reducing the risk of heart disease. This eating plan is rich in monounsaturated fats, omega-3 fatty acids, fiber, and antioxidants, which can help lower cholesterol levels, reduce inflammation, improve blood vessel function, and decrease the risk of cardiovascular events like heart attacks and strokes.
By following the Mediterranean diet, individuals can promote heart health and overall well-being.
DASH Diet
The DASH diet, which stands for Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension, is a nutritional plan designed to lower blood pressure and improve heart health. It emphasizes consuming fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and low-fat dairy while limiting foods high in saturated fats, cholesterol, and sodium.
Comparison with Other Nutrition Plans
The DASH diet is often compared to other heart-healthy nutrition plans like the Mediterranean diet. While both emphasize whole foods and limit processed foods, the DASH diet specifically focuses on reducing sodium intake, making it particularly effective in managing high blood pressure.
Recommended Daily Servings in the DASH Diet
- Fruits: 4-5 servings per day
- Vegetables: 4-5 servings per day
- Grains: 6-8 servings per day
- Lean Proteins (such as poultry, fish, beans, and nuts): 6 or fewer servings per day
- Dairy (low-fat or fat-free): 2-3 servings per day
- Fats and Oils: 2-3 servings per day
- Sweets: 5 or fewer servings per week
Plant-Based Diet
A plant-based diet is a nutrition plan that focuses on whole, minimally processed plant foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, seeds, and legumes. This diet is rich in nutrients like fiber, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, which are beneficial for heart health.
Benefits of a Plant-Based Diet for Heart Health
Switching to a plant-based diet can have numerous benefits for heart health, including:
- Lowering cholesterol levels: Plant-based foods are naturally cholesterol-free and low in saturated fats, which can help reduce LDL (bad) cholesterol levels and improve heart health.
- Reducing blood pressure: The high fiber content in plant-based foods can help regulate blood pressure and improve overall cardiovascular function.
- Managing weight: Plant-based diets are often lower in calories and saturated fats, making them an effective way to manage weight and reduce the risk of obesity-related heart issues.
Examples of Plant-Based Foods for Cardiovascular Health
Include a variety of plant-based foods in your diet to support heart health, such as:
- Leafy greens like spinach, kale, and Swiss chard
- Whole grains like quinoa, brown rice, and oats
- Legumes such as lentils, chickpeas, and black beans
- Nuts and seeds like almonds, chia seeds, and flaxseeds
- Fruits and vegetables rich in antioxidants like berries, citrus fruits, and bell peppers
Low-Sodium Diet
Maintaining a low-sodium diet is crucial in preventing heart disease as excessive sodium intake can lead to high blood pressure, which is a major risk factor for heart problems. By reducing sodium in your diet, you can effectively lower your blood pressure and decrease the strain on your heart.
Importance of a Low-Sodium Diet
- Excessive sodium intake can lead to high blood pressure.
- High blood pressure is a major risk factor for heart disease.
- Reducing sodium in your diet can help lower blood pressure and decrease strain on the heart.
Tips for Reducing Sodium Intake
- Avoid processed and packaged foods, as they are often high in sodium.
- Read food labels and choose low-sodium or sodium-free options.
- Use herbs, spices, and citrus juices to flavor your food instead of salt.
- Rinse canned vegetables and beans to remove excess sodium.
- Cook meals at home to have better control over the amount of sodium in your diet.
High-Sodium Foods to Avoid
- Canned soups
- Processed meats (e.g., bacon, deli meats)
- Packaged snacks (e.g., chips, pretzels)
- Fast food and restaurant meals
- Canned vegetables
Ultimate Conclusion
In conclusion, the significance of adopting top nutrition plans for heart health cannot be overstated. By incorporating these dietary strategies into your daily routine, you are taking proactive steps towards safeguarding your heart and overall well-being. Embrace the power of nutrition to nurture your heart and live a heart-healthy life.
Quick FAQs
What role does nutrition play in maintaining heart health?
Nutrition plays a vital role in maintaining heart health by providing essential nutrients that support cardiovascular function and help reduce the risk of heart disease.
How can the Mediterranean diet benefit heart health?
The Mediterranean diet is rich in heart-healthy foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and olive oil, which have been linked to lower rates of heart disease.
What is the recommended daily sodium intake for a low-sodium diet?
The recommended daily sodium intake for a low-sodium diet is typically around 1,500-2,300 milligrams to help prevent heart disease and manage blood pressure.

